Fuse Box Testing and Replacement Services
Fuse Box and Consumer Unit Replacement: Cost and Process by a Local Electrician Near You
If you are experiencing tripping circuits, flickering lights, or other electrical issues, it might be time to replace your old fuse box or consumer unit. Our team of qualified electricians offers reliable and cost-effective fuse box and consumer unit replacement services near you.
The cost of a fuse box or consumer unit replacement depends on several factors such as the type of unit, the number of circuits, and the complexity of the installation. Our team will provide you with a detailed quote and explain the whole process from start to finish.
Don’t let electrical problems disrupt your daily routine, contact us to book an appointment with a local electrician near you. We are committed to providing the best electrical services and solutions to our customers.
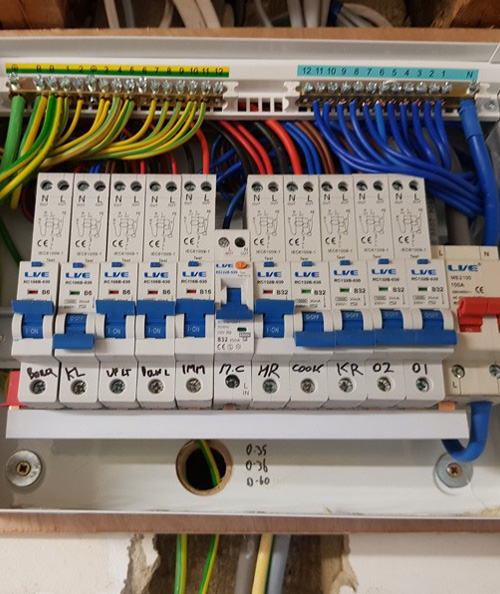
Differences Between a Fuse Box and an Electrical Consumer Unit
A fuse box and an electrical consumer unit are actually the same thing, but the term “fuse box” is an older term and is used less commonly nowadays. The electrical consumer unit is a more modern device used in homes in the UK to distribute and protect the electrical circuits. It contains a main switch and a number of miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) or residual current devices (RCDs) that provide protection to individual circuits. The term “consumer unit” is used to reflect the fact that the unit is designed to protect the consumer or end user of the electricity supply.
Do you think it's time to replace your old fuse box?
Can You Tell If Your Home Has an Old-Fashioned Fuse Box?
Determining if you have an old-fashioned fuse box involves looking for some distinctive features. If your fuse box is made of cast iron or a type of plastic, then it is most likely an older model. Another sign is if the fuses are round and have a visible wire. Modern electrical consumer units, on the other hand, use miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) or residual current devices (RCDs) instead of fuses. If you are unsure, it is best to consult with a qualified electrician.
A List of Old and New Types of Consumer Units in the UK
In the UK, there are two main types of consumer units, which include:
Old-Style Fuse Boxes:
- Wire Fuse (Wylex)
- Plug-In MCB (MEM)
- Cartridge Fuse (MEM)
Modern Consumer Units:
- Split Load Consumer Unit
- High Integrity Consumer Unit
- Dual RCD Consumer Unit
- Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) Consumer Unit
- Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection (RCBO) Consumer Unit

Do you think it's time to replace your old fuse box?
What type of consumer unit is suitable for my UK house
According to BS7671 regulations in the UK, the consumer unit for your house should meet certain standards, including the number of circuits and residual current devices (RCDs) required. The number of circuits will depend on the size and complexity of your home, while the RCDs are needed for safety reasons to detect electrical faults and cut off the power. It is recommended to consult with a qualified electrician to determine the appropriate consumer unit for your house.
What is the cost of replacing a fuse box or electrical consumer unit?
The cost of replacing a fuse box or electrical consumer unit can vary depending on the size of the property and the type of unit being installed. On average, the cost for a basic replacement can range from £500 to £700, while a more complex installation with additional features can cost upwards of £1,000. It is recommended to get a quote from a qualified electrician to get an accurate cost estimate for your specific needs.
Replacing just the consumer unit typically includes disconnecting and removing the old unit, installing and connecting a new unit, testing the system to ensure proper function, and providing necessary certification or documentation. Any necessary upgrades or modifications to the existing electrical system may also be included in the cost of the replacement. However, any additional work required to bring the system up to code or to address any pre-existing electrical issues would be an extra cost.
Frequently Asked Question
When replacing a consumer unit in a dwelling in England and Wales, it is required to obtain a certificate for compliance with Part P of the Building Regulations. This is because it is considered notifiable work. Additionally, some contractors have encountered issues where they are unable to re-energize a particular circuit after the replacement due to pre-existing defects.
The time it takes to replace a consumer unit can vary depending on the complexity of the installation, as well as any unforeseen issues that may arise during the process. In general, it can take anywhere from 3 to 6 hours on average, but this can vary based on the specific circumstances of the job.
A consumer unit can trip out for a variety of reasons, including:
- Overloading – too many electrical devices being used at the same time can overload the circuit and cause the consumer unit to trip.
- Short circuit – a short circuit occurs when a live wire comes into contact with a neutral wire, causing a sudden surge of electricity that trips the circuit.
- Faulty appliances – a faulty appliance can cause a short circuit or an overload, leading to the consumer unit tripping.
- Earth fault – an earth fault can occur when a live wire touches a metal component in an appliance or in the wiring, causing a current to flow to earth and tripping the consumer unit.
- Wiring problems – faulty or damaged wiring can cause the consumer unit to trip.
If a consumer unit is tripping frequently, it is recommended to seek the assistance of a qualified electrician to diagnose and rectify the issue.
To identify which socket is tripping the RCD, follow these steps:
- Unplug all electrical devices from the sockets on the circuit.
- Reset the RCD by pushing the switch back up.
- Plug one device back in and turn it on.
- If the RCD trips again, unplug the device and try the next one.
- Repeat the process until the RCD does not trip.
- Once you have identified the device that is causing the issue, have it checked by a qualified electrician or replace it if necessary.
If the RCD trips again even after all the devices have been unplugged, the issue could be with the wiring or the RCD itself, and it’s best to contact a qualified electrician for further inspection and repairs.

